“When George and Gerrie Andrews climbed their first Maya pyramid in the late 1950s, they hardly could have anticipated that a life’s calling was awaiting them.” That’s how I introduced the digital exhibition, “Their Maya Story: George and Gerrie Andrews,” which just went live on the UT Libraries website.
What I “hardly could have anticipated” was the variety of experience I would gain by curating this exhibition. I intended the project to enhance my skills in archival arrangement and description and to allow me to work more closely with digitization, metadata standards, Internet applications, curation, and outreach. And I did all these things, but these are fairly broad terms when it comes to information work. The specifics are where it got interesting.
I learned that you can never really be completely done with processing a series—more records always materialize. I now can scan photographic slides with confidence. Adobe Bridge became a valuable resource as I automated the conversion of dimensions, format, and resolution of digital image files. As I planned the exhibition, conversation with Mayanists gave me a clearer idea of what interested them about the archives. Crafting narrative that works as a whole or in snippets was a new kind of writing challenge. To prepare sound clips, I used Audacity and made my first foray into working with audio. I discovered the ins and outs of Drupal’s exhibit module.
In short, I learned about the wide variety of work that goes into planning and executing a digital exhibition. Too often we think of the Web as a shortcut, an easy way to make information accessible to many. And the Web does offer a great resource for increasing awareness of archival collections such as the George F. and Geraldine D. Andrews papers. But presenting information online in an engaging way, one that takes advantage of the flexibility of the interactive model, is a lot of work. As exhibition curator, I can guide you gently in the direction I think you should go and tell you what I think is interesting, but your experience with the exhibit is really up to you. That’s true in a physical museum setting, but even more so online.
To learn more about the Andrews papers, read my previous post, Adventures in Mayaland—or just visit the exhibit! Explore sites ranging from Tikal to Hormiguero, learn about the Andrews’ research methods and legacy, and simply enjoy beautiful images of Maya architecture and the story of a couple that devoted their lives to documenting this history.
Images from top, left to right:
Tikal: The man in the portal helps comprehend the scale of this roofcomb at Tikal (1981)
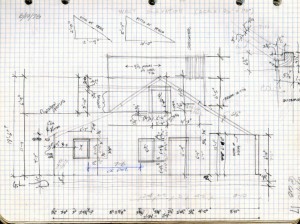
Kabah: George Andrews often traced over his photos as he attempted to understand the different styles of decoration (undated)
Tulum: The Andrews’ son, Alan, joined them for this trip to Tulum in 1964
Hormiguero: One of the many “monster masks” seen at Hormiguero (1978)
Coba: Stelae such as this one at Coba help scholars better understand Maya hieroglyphs and mythology (1978)
By Amanda Keys, processing assistant in the Alexander Architectural Archive and School of Information student focusing on archival enterprise and special collections