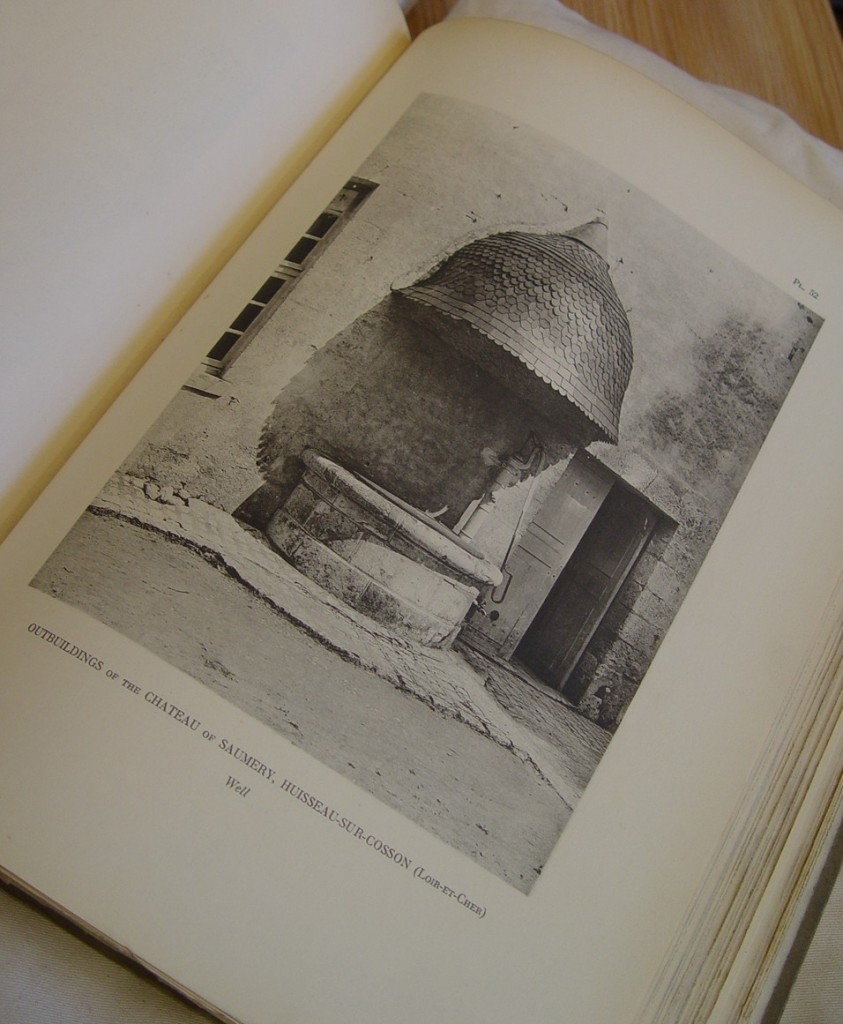
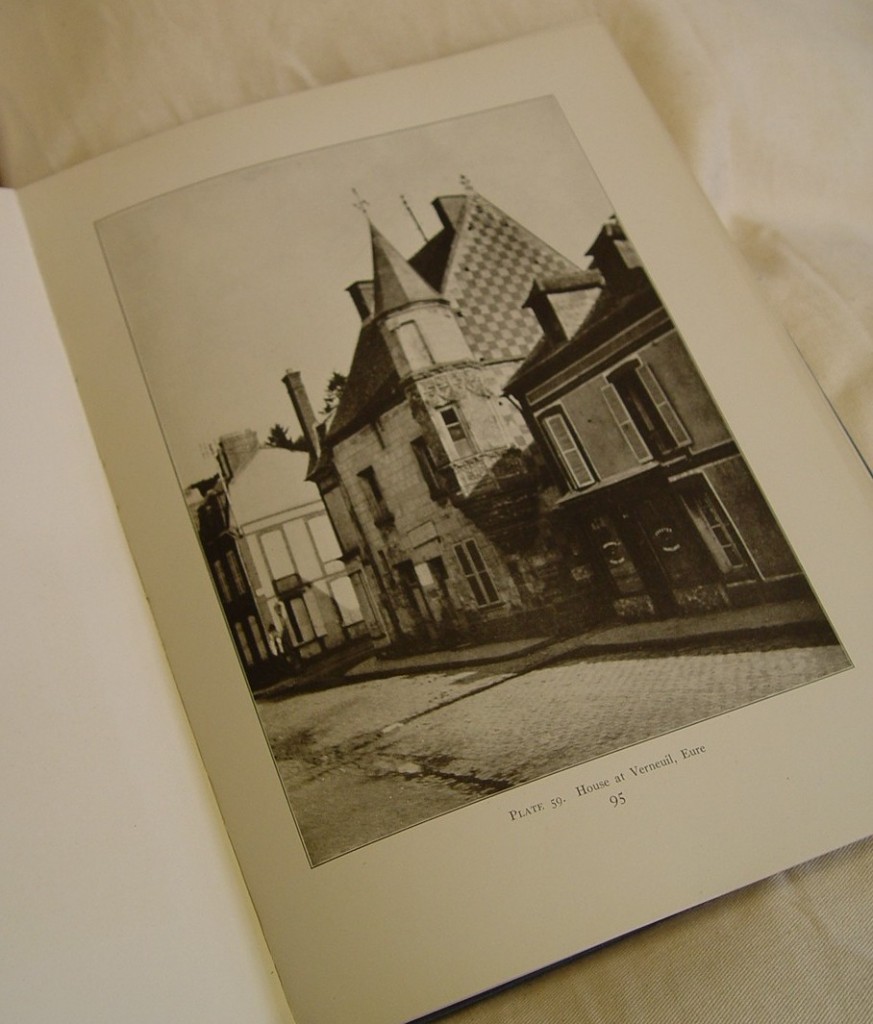
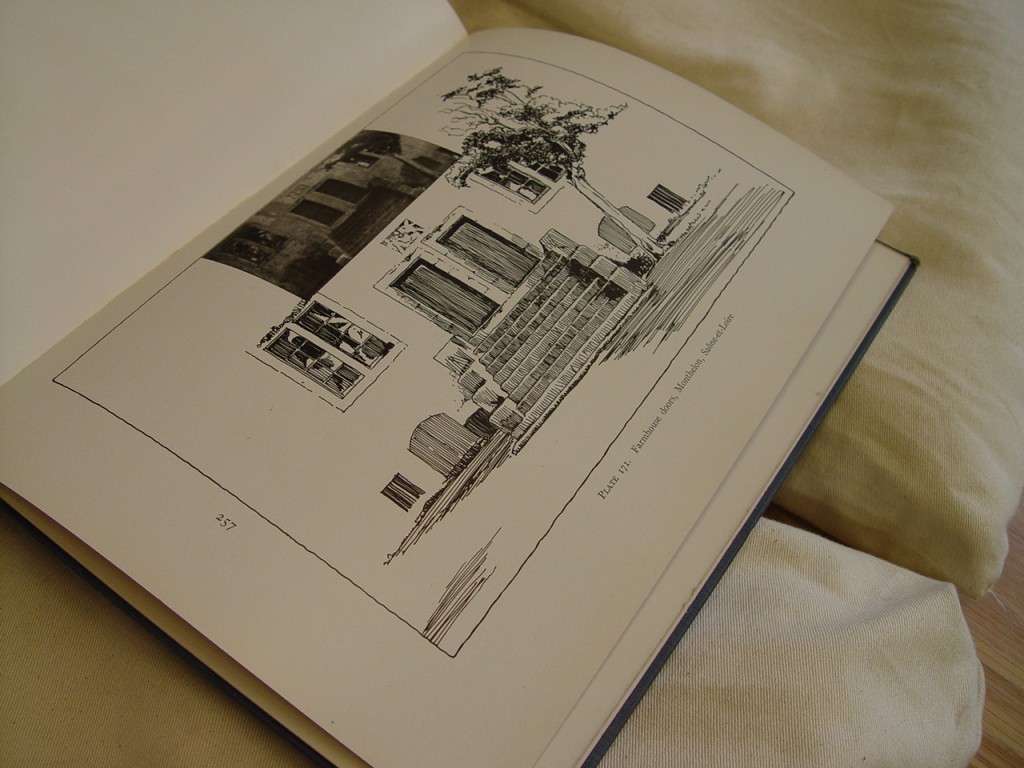
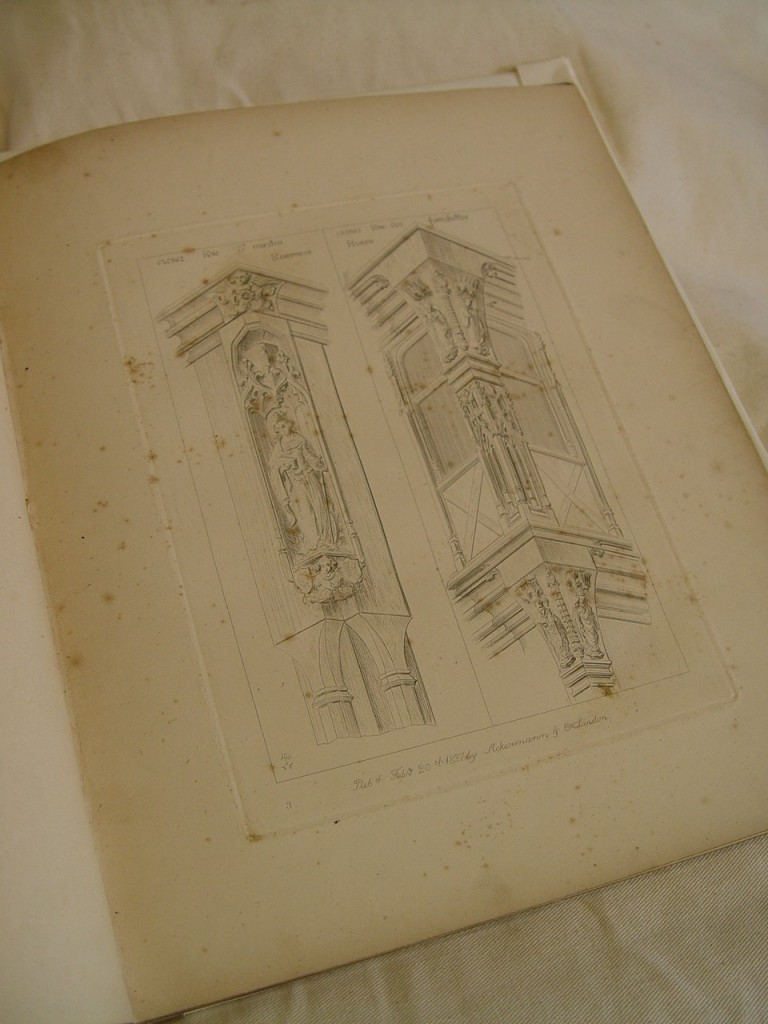
Now one of the largest repositories of its kind in the United States and housed at UT-Austin’s venerable Battle Hall, the Alexander Architectural Archives began as an associate professor’s private passion, an ad hoc gathering of student reports written for the “Survey of Texas Architecture” course taught by archives namesake Blake Alexander (1924-2011). For the class, which Alexander, a Texas native and Longhorn alum, began teaching in the 1960s, students were sent into the field and also into reading rooms of city and county libraries and archives across the Lone Star State to research land titles, conduct oral interviews, and photograph and make measured drawings of Texas buildings. Students wrote about and drew a wide swathe of edifices, some of which no longer stand, lost to indifference or to the vested interests of urban developers; some of which are currently under threat, like Austin’s Palm School, named for 19th-century Swedish immigrant Swante Palm, a diplomat and bibliophile whose donated book collection essentially started the University of Texas’ library system and whose house stood just off Congress Avenue, right where the thermal-glass tower Texas Monthly calls home now looms; and some of which, through the rugged persistence of high-minded preservationists like Alexander and his indefatigable colleague Wayne Bell, have been saved from the wrecking ball and repurposed, like the old Lone Star Brewery complex in San Antonio that today is the San Antonio Museum of Art. Buildings grand and mundane, commissioned and vernacular, everything from aristocratic 19th-century hotels to lowly log jails, were documented by students in these class reports, which were kept personally over the years by Alexander until the collection outgrew both his office and a storage room known as “Alexander’s closet” and were transferred to the care of what is now The University of Texas Libraries.
Since then, the Alexander Architectural Archives has grown into a major collection of over 280,000 drawings, 1,150 linear feet of papers, and some 300,000 photographic items related to architectural projects not just in Texas but throughout the United States and abroad as well. Though now just a fraction of the archives’ total holdings, Alexander’s seed assemblage of student reports—formally the Texas Architecture Archive (TAA)—still retains a special position with both archives staff and researchers. Its materials get heavy and loving use, so to provide even better access to this signature collection, archives staff spent much of last summer and fall reviewing and updating descriptive metadata for each and every one of the nearly 1,400 student reports. When needed, these reports, filling more than 25 record storage boxes, were also individually rehoused into acid-free folders, though it should be noted that most of these reports, many of which were written over half a century ago, well before personal computers and inkjet printers became fixtures in campus dorm rooms, are in fine fettle given the high-quality, durable cotton paper (sometimes watermarked with a vintage University of Texas bookstore logo) on which students typed their final drafts. With enhanced metadata (project dates, architect names, location information) researchers will have new access points and avenues into the collection, whether they’re looking for scholarship about a well-known Texas architect (Abner Cook, Nicholas J. Clayton, James Riely Gordon, to name a few) or have more general queries about historic structures within a specific city or county.
Richer metadata has also allowed us at the archives to begin exploring different ways to visualize the collection’s wide-ranging materials, the vast majority of which are related to the built environment of Texas. For instance, we’ve been able to use Palladio, a free browser-based digital humanities toolset developed at Stanford, to map the subject locations of each student report.

Not surprisingly, most students wrote about buildings and structures in Travis County or in cities and towns a (relatively) short drive away along the I-35 corridor north to Dallas-Fort Worth or south to San Antonio, a route that roughly follows the scalloped curve of the Balcones Fault. Conversely, the map reveals how strikingly few structures west of the Hill Country were researched. The Llano Estacado of the Lubbock area or, further south of that, the Trans-Pecos region near Fort Stockton, are more onerous distances from Austin, and impecunious pupils no doubt preferred to examine historic structures closer to the Forty Acres. One of the buildings written most frequently about, the Greek Revival Neill-Cochran House, built in 1855, is just a few short blocks from Guadalupe Street, the university’s main commercial drag. The mapped reports also simply mirror well-established historical trends of 19th– and 20th-century settlement in Texas, the limits of which were always around the 98th meridian, east of which there was enough (if not plenty of) rainfall and west of which there was land so dry that it was difficult to cultivate, making both town-building and its byproduct architecture risky propositions.
Over the next few months we’ll be writing posts meant to illuminate how the Texas Architecture Archive student reports make visible this intersection between the architecture and history (natural, social, political, industrial) of the Lone Star State. Above all, the hope is that this occasional series, which we’ll call Tales from the Texas Architecture Archive (or Tales from the TAA), will convey the elemental pleasure of time spent in our archives. Whether the subject is food, transportation, entertainment, military affairs, or demographic shifts, architecture is everywhere a foil to life. It’s always there, shaping or reflecting the world at large, a locus or backdrop to the lives we lead.
One of the more delectable documents in the TAA collection is a 59-page report on the history of Austin’s Enfield Grocery. Designed by Hugo Kuehne, founding dean of UT’s School of Architecture, it was built in 1916 with barge-board trimmings by locally-renowned Swiss woodcarver Peter Mansbendel. It offered “staple and fancy groceries” until after Prohibition, when it became The Tavern, a neighborhood beer joint. (A sports bar operates there today under the same name, serving sinfully good queso burgers on kolache buns to sudsy Longhorns fans who gather to watch televised games.) For her report, written in 1987, the student interviewed one C. J. Schmid, an old-timer who recalled the motley regulars who’d drink there in the 1930s, including Mansbendel, Paul Cret, the architect who developed the UT campus master plan, and Italian-born sculptor Pompeo Coppini, who worked with Cret on UT’s Littlefield Memorial Fountain and whose bronze figures of Jefferson Davis and Woodrow Wilson were removed last August from their prominent limestone perches on UT’s South Mall. (They eventually will be on display at their new home, the Briscoe Center for American History.) In the interview, Schmid lamented that The Tavern’s current “kindergarten” clientele was objectionably green and boorish and that fellows of his advanced age therefore avoided it, as they did Scholz Garten, where the snot-nosed college kids “kind of looked ill-kept, you know, all whiskered up” and had “stringy hair, you know, kind of greasy.” As for the waitresses, Schmid opined, “soap was not their main possession.” We can see from the TAA collection’s student reports, then, that while buildings come and buildings go, some things, like griping about younger generations and the newest out-of-towners (a seemingly inexhaustible parlor game in Austin) never change.